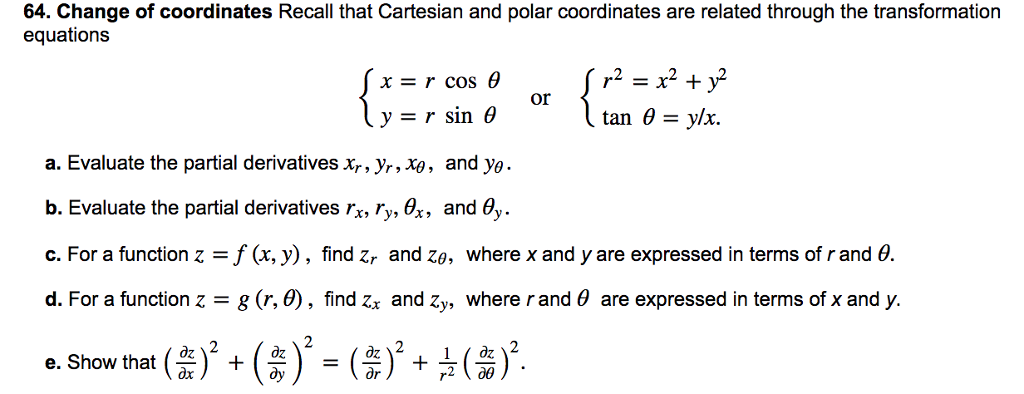
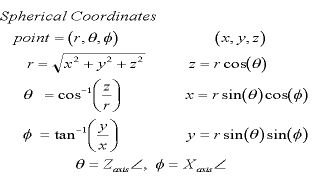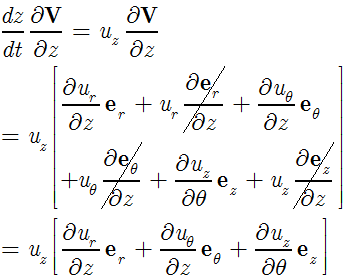complex numbers - How to evaluate this partial derivative in terms of polar coordinates - Mathematics Stack Exchange

calculus - Partial Derivatives - Chain Rule / Polar Coordinates Problem - Mathematics Stack Exchange
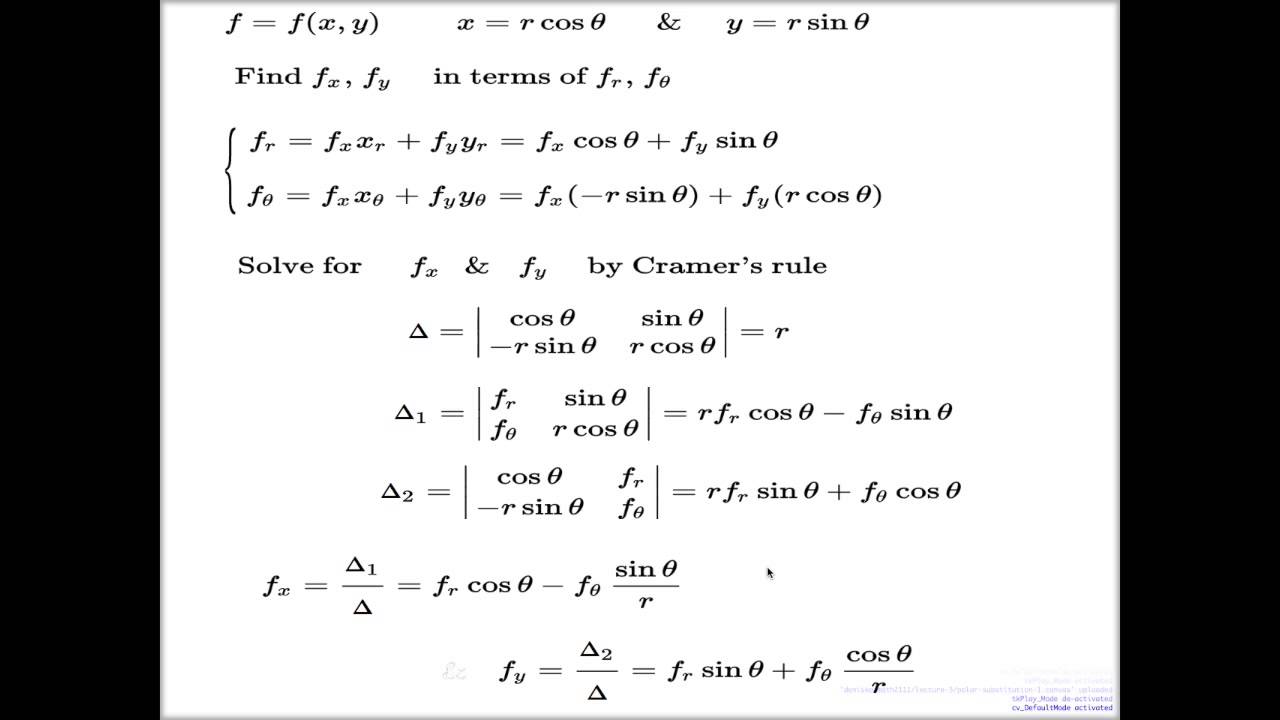
Week 3 Lecture 10 -- Chain rule examples: Cartesian and polar coordinates partial derivatives - YouTube
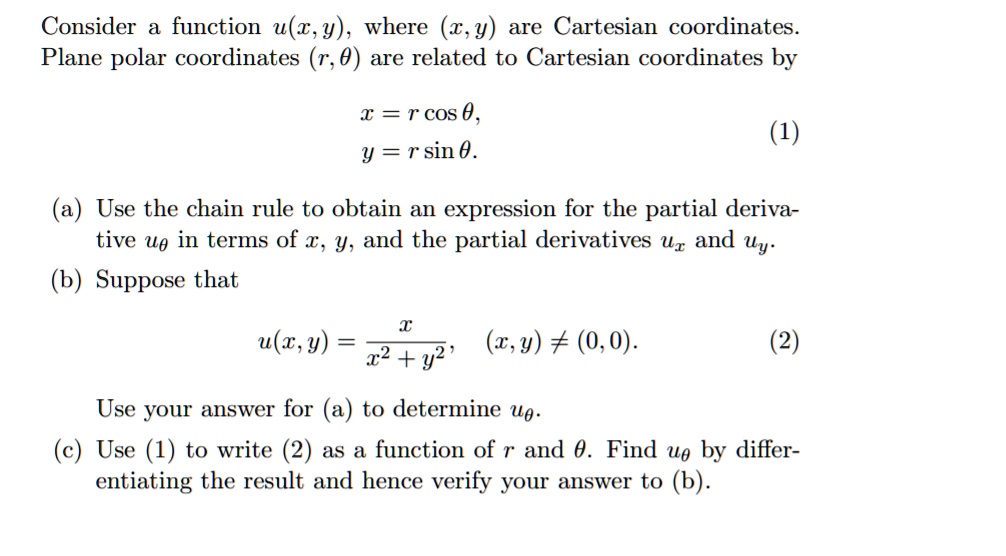
Cartesian (rectangular) coordinates (x, y) of a point can be expressed in terms of polar coordinates (r,θ) using the - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

multivariable calculus - Express partial derivatives of second order (and the Laplacian) in polar coordinates - Mathematics Stack Exchange

5.1 Definition of the partial derivative the partial derivative of f(x,y) with respect to x and y are Chapter 5 Partial differentiation for general n-variable. - ppt download
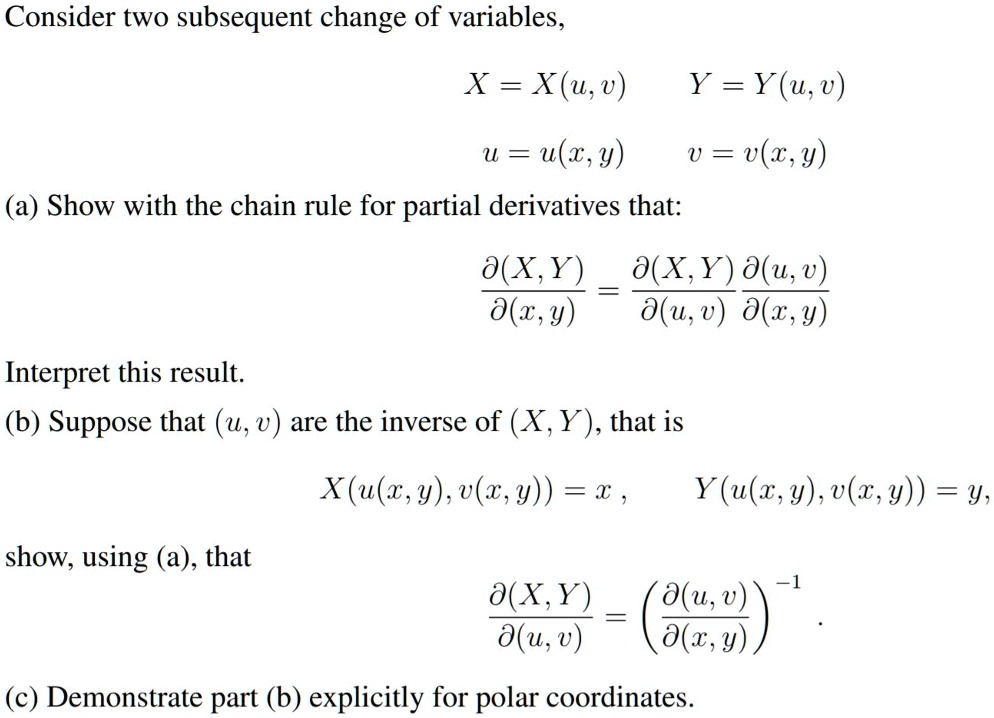
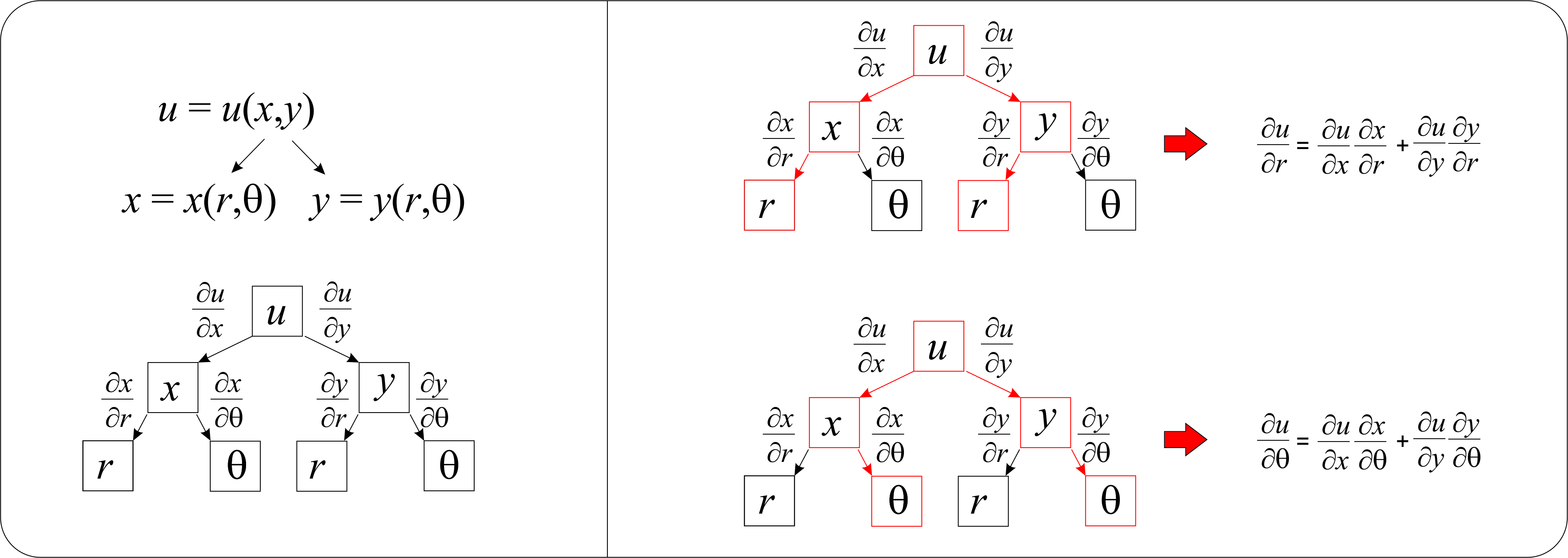
SOLVED: Consider two subsequent changes of variables: X = X(u,v) Y = Y(u,v) U = u(w,y) V = v(x,y) (a) Show with the chain rule for partial derivatives that: ∂(X,Y)/∂(u,0) = (∂X/∂u)(∂u/∂w) + (